Embedded metadata functions as the DNA of digital files, offering deeper and more comprehensive information than traditional file attributes or POSIX metadata. It is integrated directly within the file, embedding crucial insights about the file’s content, origin, and unique characteristics. Think of it as the file’s embedded biography, detailing its journey, purpose, and essence.
This intrinsic layer of information is what MetadataHub leverages, transforming raw data into actionable insights, unlocking the true value of digital assets for enhanced analysis, decision-making, and operational efficiency.

In machine-generated data, embedded metadata often constitutes the file’s critical value, serving as a treasure trove for analytics and AI initiatives. This is particularly important in data-intensive fields such as scientific research, healthcare, and industrial IoT, where metadata provides essential context.
Despite its inherent value, embedded metadata can be difficult to extract and leverage due to its close relationship with file formats. MetadataHub provides an advanced solution to this challenge.
| Traditional Methods | MetadataHub Approach |
|---|---|
| – Capture only POSIX or limited metadata – Rely on homegrown extractors (not comprehensive) – Often fail to utilize extracted metadata effectively | – Extracts comprehensive embedded metadata – Uses 400+ specialized extractors – Autonomously self-describes files – Transforms metadata into actionable insights |
MetadataHub not only extracts embedded metadata but also autonomously self-describes files, building comprehensive insights about unstructured data. By understanding both the content (what’s inside) and the context (how it was created, used, and modified), MetadataHub transforms raw files into valuable, actionable data.

Digital Images: Technical details such as camera model, aperture (f-stop), shutter speed, ISO, focal length, white balance, lens information, flash settings, GPS location, and image orientation are extracted.
Audio and Video Files: Metadata includes artist, album, codec (compression format), resolution (for video), bitrate, aspect ratio, duration, frame rate (for video), and audio channels (mono/stereo/surround).
Documents: Extracted metadata covers author information, creation/modification date, software used, document version, page and word count, security settings, font information, and access permissions.
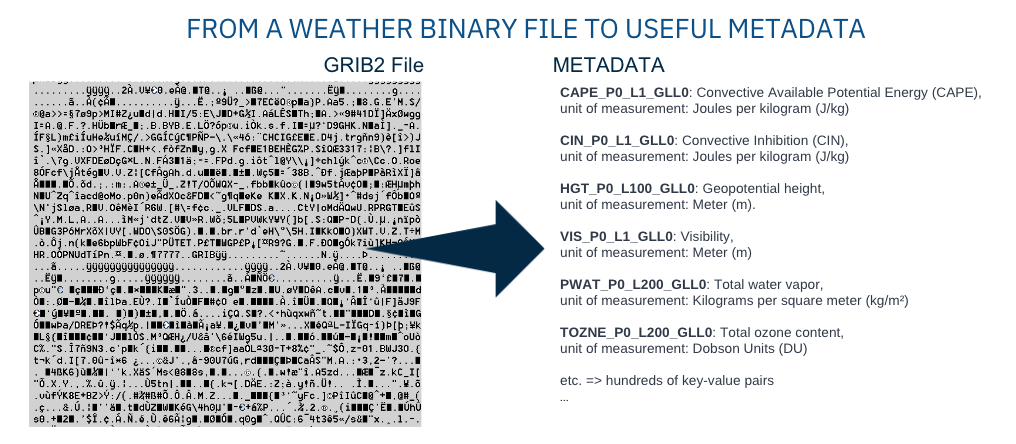
Machine-Generated Files: Includes source device information, device settings (environmental parameters, calibration), user or process identifiers, file format and structure, data quality metrics, and usage/access logs.
These technical items provide in-depth insights that enable efficient data management, analytics, and compliance monitoring.
Machine-generated metadata provides vital insights into how and under what conditions a file was produced, making it crucial for AI, IoT, and industrial applications:
MetadataHub efficiently harvests and organizes this vast range of metadata—whether from file systems or cloud storage—and provides comprehensive insights into both the content and context of unstructured data.